BIOS Settings
| Please note that this article / this category refers either on older software / hardware components or is no longer maintained for other reasons. This page is no longer updated and is purely for reference purposes still here in the archive available. |
|---|
In this article, we will explain the most important and most frequently used BIOS settings for our Supermicro and Intel motherboards.
Advanced
Various system settings can be made from the Advanced tab page of the BIOS settings screen.
Among others, the Boot, RAID and IPMI settings are configured on this page. In the following section, the individual settings options will be explained in more detail.
Boot Feature
The settings that affect the server’s boot process are located on the "Boot Feature" screen.
Quick Boot
The server boot process can be affected by the Quick Boot option. It may be set to "Disabled" or "Enabled". By default, it is "disabled" by our Quality Assurance department.
- Disabled: Each time your server is started, the hardware will perform the Power-On Self Test (POST), to exclude errors. We recommend performing this test and the Quality Assurance department enables it.
- Advantages:
- The system hardware will be tested and certain errors detected.
- Supposed error messages are no longer displayed later by the system due to proper RAM initialization (for example, The EDAC driver bug on Linux Systems).
- The BIOS may be easier to access, especially when Remote-KVM is connected to the server. When a quick boot has not been performed, the chances for accessing the BIOS by means of the [Del] key are better.
- Disadvantages:
- The boot process will require a little bit more time.
- Enabled: If the setting has been "enabled", the entire POST will not be performed completely. It will be limited to a brief testing phase.
- Advantages:
- Activation will allow your system to boot more quickly.
- Disadvantages:
- The hardware will not be tested completely.
- RAM will not be tested.
- Errors may be missed that could potentially lead to a system crash later.
- Supposed error messages may be displayed (for example, The EDAC driver bug on Linux Systems).
Quiet Boot
The boot screen can be affected by the Quiet Boot setting. It may be set to "Disabled" or "Enabled". By default, it is "disabled" by our Quality Assurance department.
- Disabled: In this case, the BIOS POST message will be displayed instead of the Supermicro & Intel logos during system startup. This setting is pre-set by the Quality Assurance department.
- Enabled: If this setting is chosen, the Supermicro & Intel logos will be seen instead of the BIOS POST message. The Tab (for Supermicro) or Esc (Intel) key will switch to displaying the BIOS POST message information. The display of the POST message information may take a while once the Tab, or Esc, key has been pressed and necessary information or POST information from the onboard controller will be skipped.
Power Configuration
- AC Power Loss
- Using this setting, you can determine how the server should react to a power loss. The options for the setting are Power-On, Power-Off or Last State. The Last State option has been set by default and will restore the server to its state prior to the power loss.
- Watch Dog Function
- If the setting is enabled, the Watch Dog timer will re-boot the system when it has been inactive for more than five minutes. By default, this option is set to "Disabled". We do not recommend using it, because it may lead to unjustified re-booting of the system.
Advanced Chip Set Control
You can configure settings from the "Advanced Chip Set Control" screen, which relate to the CPU and the North or South Bridge chip sets.
North Bridge Configuration
- Intel VT-d
- Intel VT-d can be enabled from here. You can find information about Intel VT-d and help for enabling it in the Overview of the Intel VT Virtualization Features and Activating the Intel VT-d Virtualization Features articles.
IDE/SATA or SATA/Floppy Configuration
From here, you can manage the SATA connections. Among others, you have the option of enabling the RAID feature, and setting the IDE or AHCI options. Likewise, all of the devices connected to the SATA ports will be displayed here. The order of the connected devices will be different in RAID mode than in IDE mode.
- SATA#1 Configuration - Configure SATA#1 as ...
- The RAID feature for the onboard SATA controller can be activated from the BIOS. Once this feature has been enabled, you will be able to make additional RAID settings to the BIOS controller after re-booting. You can find help for enabling the RAID feature in the The most important BIOS settings for the Supermicro Motherboard article.
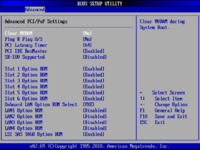
PCI/PnP Configuration
From this screen, you can configure the settings that relate to the LAN ports, the PCI slots and the onboard SAS controller.
- Load Onboard SAS Option ROM:
- If the SAS controller has been enabled, you will be able to make further RAID settings for the BIOS controller once the system has re-booted. If you do not need the onboard SAS controller, it can be disabled. The server boot process will be quicker for it, because the BIOS controller screen will not be displayed.
- You also have the option of disabling the SAS controller using a jumper.
- Load the optional Onboard LANx ROM:
- Before using the LAN ports, this setting must be enabled.
- Boots Graphic Adapter Priority:
- If a video card has been added to the system, the graphics settings must be set to the corresponding slot for the video card or "Other" depending on the BIOS. With some Supermicro motherboards, the onboard VGA controller must also be disabled using a jumper.
- PCIe Advanced Error Reporting Support (Intel only):
- The "PCI Express Advanced Error Reporting" feature can be set to "Enabled" or "Disabled". If it is set to "Enabled", the operating system will check the PCI device drivers. The messages that are returned as responses still cannot be cleanly processed by all operating systems. Our Quality Assurance department sets the feature to "Disabled" to avoid problems during operating system installation.
IPMI Configuration
From here, you can configure the "IP address", "subnet mask" and "Gateway". You can find help regarding that in the IPMI configuration through BIOS or web interface article.
Additional Information
- Switching Center – Setting up the BIOS ideally (c't 8/2008, page 174)