Setting up Veeam Replication in a VMware environment
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Veeam Backup & Replication is a backup solution and offers a range of features for performing backup tasks and disaster recovery. It is specifically designed for virtual VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V environments. This article shows how you can use Veeam Backup & Replication to create a replication task in a VMware environment.
General information
- Veeam Backup & Replication does not require an agent within the VM guest operating system for the replication process as it uses VMware's snapshot functionality to replicate data.[1]
- The VM Snapshot can be viewed as a continuous point-in-time state of a VM, including the configuration of the guest operating system, OS, applications, and files.
- Similar to an incremental backup, a complete image of the original VM is transferred to the target host during the first replica cycle.
- All subsequent replication cycles are incremental, and Veeam Backup & Replication only transfers data blocks that have changed since the last job was run. Veeam uses Changed Block Tracking technology for this.
- With Veeam Backup & Replication you can orchestrate replicas for HA purposes within a site or remote replication across sites for DR purposes.
- To enable replication over WAN links or slow connections in general, Veeam uses technologies such as deduplication and compression to optimize traffic.
- WAN Accelerators and QOS-like technologies such as Network Throttling also enable fair distribution and efficient use of available resources.
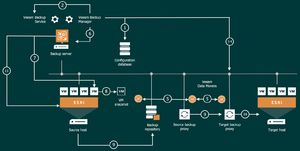
Detailed description of the replication process
The flow of a replication process with Veeam is as described below:
- Veeam Backup Manager creates a separate task for each drive to be processed in the replication process.
- Veeam Backup Manager connects to Veeam Backup Service, which includes a resource scheduling component that manages all tasks and resources in the backup infrastructure.
- Veeam Backup Manager connects to the Veeam Data Mover Services on the backup proxies and backup repository and sets a set of rules for data transfer, such as throttling network traffic, etc.
- The source Veeam Data Mover connects to the destination Veeam Data Mover and Veeam Data Mover on the backup repository
- Veeam Backup Manager queries information about VMs and ESXi hosts from Veeam Broker Service.
- When Application Consistent Processing is enabled, Veeam connects to the guest operating system and runs a "runtime process" to enable Application Consistent Processing.
- Veeam Backup & Replication triggers the creation of a VM snapshot through the vCenter Server or ESXi host, putting each VMDK in a read-only state and creating an additional delta file per VMDK. All changes that occur within the VM during replication are written to the delta file.
- During replication, the source Veeam Data Mover reads the data from the VM disk and copies it. During a subsequent replication, Veeam uses the CBT information to filter out only the blocks that have changed since the last replication. If CBT information is missing, Veeam uses the information from metadata stored in the repository to detect changed blocks. During the copy process, the source data mover filters out empty blocks, swap files and excluded data to optimize the transfer process. In addition, the data mover compresses the data traffic towards the target data mover.
- The data mover on the target side unpacks the data and writes it to the repository.
- After the proxy completes the read operation, a snapshot commit prompt is sent to the vCenter or ESXi host to consolidate the snapshot.
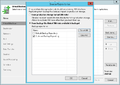
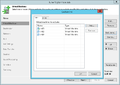
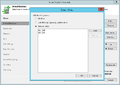
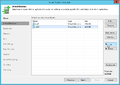
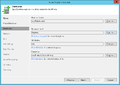
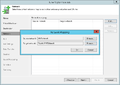
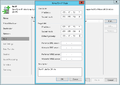
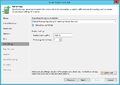
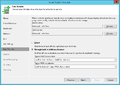
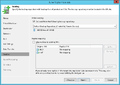
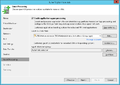
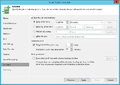
Creation of a replication job
The following section shows how to create a replication job:[2]
References
- ↑ About Replication - Veeam Backup Guide for VMware vSphere (helpcenter.veeam.com)
- ↑ Creating Replication Jobs - Veeam Backup Guide for VMware vSphere (helpcenter.veeam.com)
Related articles
Veeam Replica Failover and Failback functionality