Consumer versus Enterprise SSDs
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are available in two variants: Client SSDs for the consumer sector and Enterprise SSDs for the server sector. While client SSDs are designed for eight hours of operation per day and optimized costs, enterprise SSDs are optimized for 24/7 operation and the highest levels of data reliability, availability and integrity. These and other differences between the two model variants are shown in the table in this article.
Consumer SSDs compared to Enterprise SSDs
The following table shows the most important differences between client and enterprise SSDs.
| Consumer/Client SSD | Enterprise SSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Application area | PCs | Server | |
| Optimized for[1] |
|
| |
| JEDEC SSD
Requirements & Endurance Test Method[2] |
Workload / Application Class[1] | Client Workload:
|
Enterprise Workload:
|
| Active Use (Power on) | 8h/day at 40°C | 24h/day at 55°C | |
| Data Retention | 1 year at 30°C | 3 months at 40°C | |
| UBER (Unrecoverable Bit Error Ratio) | ≤ 10-15 | ≤ 10-16 | |
| TBW (Terabytes written) resp. DWPD specification | according to Client Workload | according to Enterprise Workload | |
| Comparability TBW/DWPD Client/Enterprise |
| ||
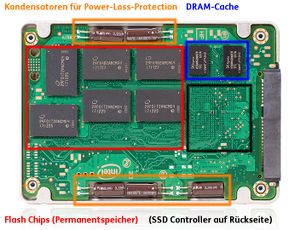
| SSD Power Loss Protection[3] | - | ✔ | |
| Operation on Hot-Swap Backplane[4] | Not recommended by Thomas-Krenn | ✔ | |
| Typical manufacturer warranty | 3 years | 5 years | |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 JEDEC SSD Endurance Workloads (Flash Memory Summit 2011)
- ↑ Solid State Drive (SSD) Requirements and Endurance Test Method (www.jedec.org)
- ↑ Typically, client SSDs are not equipped with power loss protection, mainly for cost reasons. Enterprise SSDs usually have power loss protection. Individual exceptions are possible in both areas.
- ↑ The use of a hot-swap backplane results in an additional plug connection in the data path. Client SSDs, which are designed for operation on a direct cable connection, generally tolerate reflections caused by this less than Enterprise SSDs.
|
Author: Werner Fischer Werner Fischer, working in the Knowledge Transfer team at Thomas-Krenn, completed his studies of Computer and Media Security at FH Hagenberg in Austria. He is a regular speaker at many conferences like LinuxTag, OSMC, OSDC, LinuxCon, and author for various IT magazines. In his spare time he enjoys playing the piano and training for a good result at the annual Linz marathon relay.
|