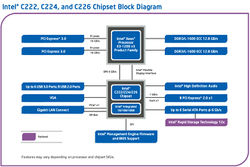
Chipsety Intel C220
Przejdź do nawigacji
Przejdź do wyszukiwania
Chipsety Intel C220 (nazwa kodowa Lynx Point) wykorzystywane są w serwerach single CPU i płytach głównych pod procesory Intel Xeon E3-1200 v3 (mikroarchitektura Haswell). Są one następcami chipsetów C200, które były wykorzystywane z procesorami Sandy Bridge i Ivy Bridge.
Przegląd chipsetów C220
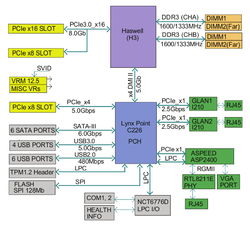
Płyta główna Supermicro X10SLH-F z chipsetem Intel C226 korzysta z Flexible I/O w celu udostępnienia 6 portów SATA 6Gb/s.
Seria C220 składa się z trzech chipsetów:
| C222 | C224 | C226 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible I/O | - | - | ✔ |
| PCI Express porty 2.0 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
Suma portów USB
|
10 2 8 |
12 4 8 |
14 4-6(*) 10-8(*) |
Suma portów SATA
|
6 2 4 |
6 4 2 |
4-6(*) 4-6(*) 0 |
| VGA | - | - | ✔ |
| Intel Wireless Display | - | - | ✔ |
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology - AHCI | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology - obsługa RAID 0/1/5/10 | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Intel Rapid Storage Technology - Intel Smart Response Technology | - | - | ✔ |
| Intel Active Management Technology 9.0 | - | - | ✔ |
| Intel Identity Protection Technology (Intel IPT) | - | - | ✔ |
(*) w zależności od konfiguracji Flexible I/O projektantów płyty głównej
Innowacje w porównaniu do C200
Generacja chipsetów C220 oferuje następujące innowacje:[1]
- USB 3.0
- Intel Flexible I/O
- Intel Rapid Storage Technology 2.0
- Do 6 portów SATA 6Gb/s
- PCI Express Latency Tolerance Reporting (LTR)
- The root port supports the extended Latency Tolerance Reporting (LTR) capability.
- LTR provides a means for device endpoints to dynamically report their service latency requirements for memory access to the root port.
- Endpoint devices should transmit a new LTR message to the root port each time its latency tolerance changes (and initially during boot).
- The PCH uses the information to make better power management decision.
- The processor uses the worst case tolerance value communicated by the PCH to optimize c-state transitions.
- This results in better platform power management without impacting endpoint functionality.
- Endpoint devices the support LTR must implement the reporting and enable mechanism detailed in the PCIe* Latency Tolerance Reporting Engineering Change Notice.
- Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- Quad IO Fast Read, Quad Output Fast Read, Dual IO Fast Read
- TPM over SPI
- Serial Flash Discoverable Parameter (SFDP)
Odnośniki
- ↑ Intel® 8/C220 Series Chipset Platform Controller Hub: Datasheet (www.intel.com)
Dalsze informacje
- Wandelbare Verwaltungsmaschine Das leistet die „Management Engine“ in Intel-Chipsätzen (c't 13/2014, Seite 138)
- Intel® Xeon® Processor E3-1200 v3 Product Family with Intel® HD Graphics P4600 and Intel® C226 Chipset (www.intel.com)
- Intel Xeon Processor E3-1200 v3 Product Family-based Platforms for Intelligent Systems (www.intel.com)
- 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor-Based Platforms for Intelligent Systems (www.intel.com)
- Haswell-based Xeon chipsets (en.wikipedia.org)
Autor: Thomas Niedermeier
Powiązane artykuły
Aktualizacja mikrokodu firmy Intel w Linuksie
Luki bezpieczeństwa Spectre-NG (Spectre Next Generation)
Zalecenia dotyczące bezpieczeństwa produktów firmy Intel 2020-11-10 2020.2 IPU