Aktualizacja mikrokodu procesorów firmy Intel w FreeBSD
FreeBSD umożliwia aktualizację mikrokodu procesora na etapie uruchamiania lub w czasie działania systemu. W tym artykule, korzystając z serwera z FreeBSD 12.0, chcemy pokazać, jak można sprawdzić aktualną wersję mikrokodu firmy Intel i w razie potrzeby zainstalować nowszą wersję mikrokodu.
Konfiguracja testowa
W tym przykładzie została wykorzystana następująca konfiguracja:
- Serwer z płytą główną ASUS P9D-MV z BIOS-em w wersji 2101 i procesorem Intel Celeron G1820T
- FreeBSD 12.0
Poniższy przykład został przeprowadzony 16.01.2019 r. z aktualnymi w tym czasie wersjami BIOS-u, mikrokodu i oprogramowania. Przedstawia on, jak w środowiskach o krytycznym znaczeniu dla bezpieczeństwa może zostać przeprowadzona aktualizacja mikrokodu i aktualizacje bezpieczeństwa.
Odczyt aktualnej wersji mikrokodu
Informacje o CPU (nazwa, CPUID, wersja mikrokodu) można uzyskać za pomocą narzędzia x86info po załadowaniu modułu cpuctl:
kldload cpuctlx86info -a
W wierszu Microcode version jest widoczna wersja (w przykładzie 0x00000000000000000024), CPUID znajduje się w drugim wierszu eax (w przykładzie 000306c3):
root@freebsd12:~ # kldload cpuctl root@freebsd12:~ # x86info -a x86info v1.31pre MP Table: # APIC ID Version State Family Model Step Flags # 0 0x15 BSP, usable 6 12 3 0x0381 # 2 0x15 AP, usable 6 12 3 0x0381 Found 2 identical CPUs Extended Family: 0 Extended Model: 3 Family: 6 Model: 60 Stepping: 3 Type: 0 (Original OEM) CPU Model (x86info's best guess): Xeon E3 [Haswell] Processor name string (BIOS programmed): Intel(R) Celeron(R) CPU G1820T @ 2.40GHz [...] Microcode version: 0x0000000000000024 eax in: 0x00000000, eax = 0000000d ebx = 756e6547 ecx = 6c65746e edx = 49656e69 eax in: 0x00000001, eax = 000306c3 ebx = 00100800 ecx = 4ddaebbf edx = bfebfbff
Więcej informacji na ten temat można znaleźć na stronie Odczyt informacji o sprzęcie w FreeBSD - x86info.
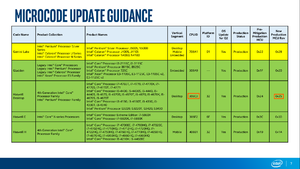
Intel udostępnia informacje o dostępnych wersjach mikrokodu w dokumencie Microcode Update Guidance ( vide Intel Microcode - wersje mikrokodu). W tym dokumencie procesory są wymienione według CPUID.
Szukając 306c3 w Microcode Update Guidance z 08.08.2018, w kolumnie New Production MCU Rev znajduje się mikrokod w wersji 0x25. W tym przypadku Intel dostarcza nowszą wersję mikrokodu niż obecnie dostępna w BIOS-ie testowego systemu.
Wariant 1: Update via devcpu-data
Port devcpu-data zawiera aktualizacje mikrokodów dla procesorów Intel i AMD (pliki binarne). Mikrokody z devcpu-data są wprowadzane do procesora poprzez cpuctl(4) / cpucontrol(8). Aby aktualizacja mikrokodu była przeprowadzana automatycznie podczas uruchamiania, wpisy cpu_microcode_load i cpu_microcode_name muszą zostać dodane do /boot/loader.conf.
Aby w przyszłości automatycznie instalować aktualizacje mikrokodu, należy zainstalować pakiet devcpu-data i następnie wprowadzić dwie wymienione opcje w /boot/loader.conf:
# pkg install devcpu-data # vi /boot/loader.conf # cat /boot/loader.conf cpu_microcode_load="YES" cpu_microcode_name="/boot/firmware/intel-ucode.bin" # reboot
Na testowym systemie, wersja mikrokodu jest aktualizowana z 0x24 do 0x25:
root@freebsd12:~ # pkg install devcpu-data [...] Message from devcpu-data-1.20: Installing this port will allow host startup to update the CPU microcode on a FreeBSD system automatically. There are two methods for updating CPU microcode: the first methods loads and applies the update before the kernel begins booting, and the second method loads and applies updates using an rc script. The first method is preferred, but is currently only supported on Intel i386 and amd64 processors running FreeBSD 12.0. It is safe to enable both methods. The first method ensures that any CPU features introduced by a microcode update are visible to the kernel. In other words, the update is loaded before the kernel performs CPU feature detection. To enable updates using the first method, add the following lines to the system's /boot/loader.conf: cpu_microcode_load="YES" cpu_microcode_name="/boot/firmware/intel-ucode.bin" This method will not load the microcode update until the system is rebooted. To enable updates using the second method, add the following line to the system's /etc/rc.conf: microcode_update_enable="YES" Then, to ensure the update is applied, reboot the system or start the microcode update service via: # service microcode_update start If the CPU requires a microcode update, a console message such as the following will appear: Updating CPU Microcode... /usr/local/share/cpucontrol/m32306c3_00000022.fw: updating cpu /dev/cpuctl0 from rev 0x17 to rev 0x22... done. /usr/local/share/cpucontrol/m32306c3_00000022.fw: updating cpu /dev/cpuctl2 from rev 0x17 to rev 0x22... done. /usr/local/share/cpucontrol/m32306c3_00000022.fw: updating cpu /dev/cpuctl4 from rev 0x17 to rev 0x22... done. /usr/local/share/cpucontrol/m32306c3_00000022.fw: updating cpu /dev/cpuctl6 from rev 0x17 to rev 0x22... done. Done. root@freebsd12:~ # ls -lh /boot/firmware/intel-ucode.bin -rw-r--r-- 1 root wheel 1.7M Jan 11 23:18 /boot/firmware/intel-ucode.bin root@freebsd12:~ # vi /boot/loader.conf root@freebsd12:~ # cat /boot/loader.conf cpu_microcode_load="YES" cpu_microcode_name="/boot/firmware/intel-ucode.bin" root@freebsd12:~ # reboot [...]
Po ponownym uruchomieniu systemu nowy mikrokod jest już używany:
root@freebsd12:~ # kldload cpuctl root@freebsd12:~ # x86info -a | grep -i microcode Microcode version: 0x0000000000000025
Wariant 2: Update via cpupdate
Oprócz wariantu opisanego powyżej, od 2018 r. dostępny jest jeszcze jeden port do aktualizacji mikrokodu: sysutils/cpupdate. Został on opracowany przez Stefana Blachmanna jako alternatywa dla devcpu-data, aby uniknąć błędów i ograniczeń devcpu-data.[1][2][3] Nowe narzędzie cpupdate oferuje dodatkowe funkcje, np. proste uzyskanie informacji o aktualnym mikrokodzie poprzez cpupdate -i.[4]
Twórca zaleca samodzielne skompilowanie narzędzia.[5] Ponieważ modernizacja z skompilowanych portów jest żmudna,[6] Z racji tego, że upgrade z kompilowanych portów jest pracochłonny,[7] na systemach produkcyjnych jest bardziej zalecane użycie opisanego powyżej wariantu 1 lub użycie poudriere do budowania pakietów z portów.
Instalacja cpupdate na systemie testowym może być wykonana w następujący sposób:
# portsnap auto # cd /usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # make install
Wykonane na systemie testowym:
root@freebsd12:~ # portsnap auto
root@freebsd12:~ # cd /usr/ports
root@freebsd12:/usr/ports # make search name=cpupdate
Port: cpupdate-g20180513_1
Path: /usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate
Info: CPU microcode update utility for x86
Maint: eugen@FreeBSD.org
B-deps:
R-deps:
WWW: https://github.com/kernschmelze/cpupdate
root@freebsd12:/usr/ports # cd /usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate
root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # make install
===> Building/installing dialog4ports as it is required for the config dialog
[...]
┌─────────────────────────── cpupdate-g20180513_1 ─────────────────────────────┐
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │+[x] CPM Download platomav/CPUMicrocodes collection │ │
│ │+[x] INTEL Download Intel microcode pack microcode-20180807.tgz │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ < OK > <Cancel> │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
===> License BSD2CLAUSE accepted by the user
===> cpupdate-g20180513_1 depends on file: /usr/local/sbin/pkg - found
=> microcode-20180807.tgz doesn't seem to exist in /usr/ports/distfiles/.
=> Attempting to fetch https://downloadmirror.intel.com/28039/eng/microcode-20180807.tgz
microcode-20180807.tgz 1591 kB 7924 kBps 01s
[...]
Installing cpupdate-g20180513_1...
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
NOTE: The following directories
/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate/work/CPUMicrocodes-0d88b2e
/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate/work/intel-ucode
contain Intel and/or platomav/CPUMicrocodes collections respectively
if you have just built the port with corresponding CPM/INTEL option(s) enabled.
In this case you can run "make install-microcodes" to install them to
/usr/local/share/cpupdate
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Suspend/resume sequence clears microcode update, so make sure your system runs
"service cpupdate start" again on resume.
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # make install-microcodes
/bin/rm -f -rf /usr/local/share/cpupdate/CPUMicrocodes/primary/Intel
/bin/mkdir -p /usr/local/share/cpupdate/CPUMicrocodes/primary/Intel
[...]
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
NOTE: you have to manually remove the directory
/usr/local/share/cpupdate/CPUMicrocodes/primary/Intel
after deinstallation of cpupdate.
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
NOTE: you have to manually remove the directory
/usr/local/share/cpupdate/CPUMicrocodes/secondary/Intel
after deinstallation of cpupdate.
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate #
Cpupdate oferuje następujące opcje:
# cpupdate Usage: cpupdate [-qwvvuiCXIAVh] [-<f|U> <microcodefile>] [-<cpsST> <datadir>] -i show processor information -u update microcode -U update microcode using file <microcodefile> -w write it: without this option cpupdate only simulates updating -q quiet mode -v verbose mode, -vv very verbose -p use primary repo path <datadir> -s use secondary repo path <datadir> -V print version -h show this help -IAV for the options below: vendor mode must be set [atm only Intel (-I) implemented] -f show version information of microcode file -c Check integrity of microcode files in <datadir> -d As -c, in addition print microcode file statistics -C convert/compact microcode files from legacy to multi-blob intel-ucode file format -X convert (extract) microcode files from multi-blob intel-ucode to legacy file format -S source dir for converting -T target dir for converting
Aktualizacja mikrokodu podczas pracy wygląda następująco na przykładowym systemie:
root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # cpupdate -i Found CPU(s) from Intel Core 0 to 1: CPUID: 306c3 Fam 06 Mod 3c Step 03 Flag 02 uCode 00000024 root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # cpupdate -u Found CPU(s) from Intel No updating error. Registering CPU features Successfully registered new CPU features ATTENTION NOTICE: -w option missing! No actual update, only dry run done!. root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # cpupdate -w -u Found CPU(s) from Intel No updating error. Registering CPU features Successfully registered new CPU features root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate # cpupdate -i Found CPU(s) from Intel Core 0 to 1: CPUID: 306c3 Fam 06 Mod 3c Step 03 Flag 02 uCode 00000025 root@freebsd12:/usr/ports/sysutils/cpupdate #
W celu automatycznej aktualizacji mikrokodu przy uruchamianiu wymagane są następujące kroki:
- Należy dodać następujący wpis do /boot/loader.conf:
cpuctl_load="YES"
- Dodajemy następujący wpis do /etc/rc.conf:
cpupdate_enable="YES"
- Następnie należy wykonać restart.
Po ponownym uruchomieniu cpupdate pokazuje na przykładowym systemie nową wersję mikrokodu 0x25:
root@freebsd12:~ # cpupdate -i Found CPU(s) from Intel Core 0 to 1: CPUID: 306c3 Fam 06 Mod 3c Step 03 Flag 02 uCode 00000025 root@freebsd12:~ #
Różnice
Podczas testowania obydwu wariantów w dniu 16.01.2018, zauważyliśmy, że #Wariant 1: Update via devcpu-data ładuje mikrokod bardzo wcześnie już w trakcie procesu uruchamiania.[8] Już przy pierwszej inicjalizacji procesora rozpoznawane są cztery Structured Extended Features3, (IBPB, STIBP, L1DFL, SSBD), które są zawarte w wersji mikrokodu 0x25. Oto fragment wyjścia z dmesg:
Copyright (c) 1992-2018 The FreeBSD Project. Copyright (c) 1979, 1980, 1983, 1986, 1988, 1989, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994 The Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. FreeBSD is a registered trademark of The FreeBSD Foundation. FreeBSD 12.0-RELEASE-p2 GENERIC amd64 FreeBSD clang version 6.0.1 (tags/RELEASE_601/final 335540) (based on LLVM 6.0.1) VT(efifb): resolution 800x600 CPU: Intel(R) Celeron(R) CPU G1820T @ 2.40GHz (2394.52-MHz K8-class CPU) Origin="GenuineIntel" Id=0x306c3 Family=0x6 Model=0x3c Stepping=3 [...] Structured Extended Features3=0x9c000000<IBPB,STIBP,L1DFL,SSBD> [...] real memory = 2147483648 (2048 MB) avail memory = 2002632704 (1909 MB) CPU microcode: updated from 0x24 to 0x25
W wariancie 2 z cpupdate brakuje na początku dwóch z czterech Structured Extended Features 3 - dlatego starsza wersja mikrokodu 0x24 jest nadal na początku w użyciu. Jest to widoczne w dmesg:
Copyright (c) 1992-2018 The FreeBSD Project. [...] CPU: Intel(R) Celeron(R) CPU G1820T @ 2.40GHz (2394.52-MHz K8-class CPU) Origin="GenuineIntel" Id=0x306c3 Family=0x6 Model=0x3c Stepping=3 [...] Structured Extended Features3=0xc000000<IBPB,STIBP> [...] real memory = 2147483648 (2048 MB) [...] Trying to mount root from ufs:/dev/ada0p2 [rw]... CPU: Intel(R) Celeron(R) CPU G1820T @ 2.40GHz (2394.52-MHz K8-class CPU) Origin="GenuineIntel" Id=0x306c3 Family=0x6 Model=0x3c Stepping=3 [...] Structured Extended Features3=0x9c000000<IBPB,STIBP,L1DFL,SSBD>
Wprawdzie w wariancie 2 z cpupdate również możliwe jest wczytanie mikrokodu już na początku, jednak w tym celu należy podać dokładny plik mikrokodu procesora.[9] W przykładowym systemie, jest to możliwe dzięki następującej pozycji w /boot/loader.conf:
cpu_microcode_load="YES" cpu_microcode_name="/usr/local/share/cpupdate/CPUMicrocodes/primary/Intel/06-3c-03"
Odnośniki
- ↑ Introducing cpupdate, a microcode tool for FreeBSD (forums.freebsd.org, 09.02.2018)
- ↑ cpupdate (github.com)
- ↑ Bug 192487 - cpucontrol uses unsafe procedure to detect current microcode version (bugs.freebsd.org)
- ↑ cpupdate manpage draft (bsd.denkverbot.info, 19.03.2018)
- ↑ cpupdate (github.com) Please do not install via pkg. Please use ports or manually clone it with git.
- ↑ Absolute FreeBSD 3rd Edition Chapter 16, page 371: Ports and Production: I would strongly encourage you to build build your own package repository with poudriere and manage your servers' ports from that repository. Upgrading ports directly installed on a host is annoying and difficult. [...] You have been warned.
- ↑ Absolute FreeBSD 3rd Edition Chapter 16, page 371: Ports and Production: I would strongly encourage you to build build your own package repository with poudriere and manage your servers' ports from that repository. Upgrading ports directly installed on a host is annoying and difficult. [...] You have been warned.
- ↑ D16370: Implement early microcode loading for Intel i386 and amd64 platforms (reviews.freebsd.org)
- ↑ Introducing cpupdate, a microcode tool for FreeBSD - Comment #16 (forums.freebsd.org, 16.01.2019)
Autor: Werner Fischer
