UPS Basics
A UPS (uninterruptible power supply) is a power supply system with energy storage that ensures a supply to the connected consumer in the event of a power failure. The device filters the alternating current and only then passes it on to the end device. How are the individual UPS types differentiated and for which areas of application are they used? We answer these and other questions in this article.
UPS basics
To prevent data loss, computers that manage or provide sensitive data must be protected against an unexpected power failure. This applies, for example, to servers within networks. In the event of a power failure, the servers should be protected in such a way that at least the open files can be saved and the servers can be shut down.
A UPS is connected between the mains and the load for this purpose. Rechargeable batteries (accumulators) form the core of a UPS, which guarantee the supply of power to consumers for a certain period of time in the event of a fault. Information on the dimensioning of UPS systems can be found in the article Difference between Volt-amperes and Watts.
Overview of the types of power grid faults
The following table shows the different types of grid faults, their typical duration and explanations of the events.
| Fault type | Duration of the fault | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Power Failure | > 10 ms | A power failure is defined as a zero voltage condition, this can be due to a mains voltage fault. |
| Power Sag | < 16 ms | Voltage fluctuations are dips that are briefly below the normal value. They can occur when large systems or power lines are switched on. |
| Switching Transient | 4 ms - 16 ms | These are often caused by a static discharge. Voltage peaks are also often referred to as switching peaks. |
| Power Surge | < 4 ms | These occur during sudden and brief voltage peaks. This can normally be attributed to a lightning strike in the immediate vicinity. |
| Under Voltage | ongoing | The voltage falls below the permissible limit value (for a few seconds or even permanently). |
| Over Voltage | ongoing | If, for example, large electrical systems are activated, the voltage can rise to over 100%, which is referred to as overvoltage. |
| Frequency Variation | occasionally | The frequency deviates from the normally constant mains frequency. |
| Line Noise | periodically | A voltage distortion is also referred to as an electrical interference voltage, which has a negative influence on the circuits in electrical systems. |
| Harmonic Distortion | ongoing | The normal waveform of the voltage is distorted and thus changed. This can be caused, for example, by simple fluorescent tubes that transmit this to the mains cable. |
UPS types
There are three different types of UPS:
- VFD (Voltage Frequency Dependent from Mains Supply) - Standby/Offline UPS
- VI (Voltage Independent from Mains Supply) - Line Interactive UPS
- VFI (Voltage and Frequency Independent from Mains Supply) - Online UPS
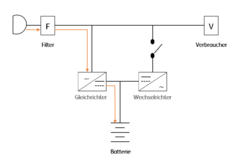
VFD (Voltage Frequency Dependent from Mains Supply)
This type of UPS, also called standby or offline UPS, is the simplest UPS. It only protects against a total mains failure. Mains voltages, fluctuations or mains frequencies cannot be compensated by them. In the event of a mains failure, a battery takes over the power supply. The system also switches to battery operation in the event of an overvoltage or undervoltage. The switching times are within a few milliseconds and are sufficient to maintain most systems. The battery is recharged during normal operation via a charging rectifier. The efficiency here is around 95%. This type of UPS is therefore often used for very small consumers or only for individual computers.
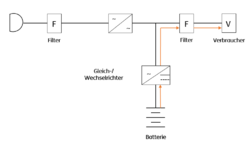
VI (Voltage Independent from Mains Supply)
This UPS, also known as a line interactive UPS, protects against a total mains failure and against fluctuations in the mains voltage. This is achieved by a voltage regulator connected between the mains input and the load. This UPS is therefore very suitable for an environment where there are many voltage fluctuations. The efficiency is between 95% and 98%. This means that individual computer systems, networks or larger telecommunications systems can be protected. Highly sensitive systems should not be equipped with it.
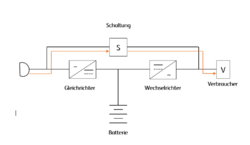
VFI (Voltage and Frequency Independent from Mains Supply)
The VFI UPS, also known as the online UPS, offers maximum protection. It compensates for fluctuations in both the mains voltage and the mains frequency. In normal operation, the load is constantly supplied via the battery. As this type of UPS does not have to switch to another operating mode in the event of a mains failure, there are no switching times compared to other types of UPS. This UPS works with a "continuous converter principle", i.e. the conversion from AC to DC voltage and from DC to AC voltage. As the voltage is constantly being converted, electrical losses and heat can occur. The efficiency is therefore 90%. Due to the continuous load, the service life of the batteries is not very long, on average 3 to 4 years. This type of UPS is therefore often found in server and data communication applications.
|
Author: Theresa Lorenz Theresa Lorenz has been with Thomas-Krenn.AG since 2013. After completing her training as an IT specialist, she assisted customers with support requests. With the experience she gained, she then switched to production and created assembly instructions and documentation for production and quality assurance processes. She is now team leader of the entire assembly team in our production department. In her free time, she enjoys sports and cultivating her friendships.
|