Virtual network interface enx of Supermicro Motherboards
On Supermicro motherboards from the X12/H12 series with RoT (Root of Trust) function, an additional, virtual network interface appears in the operating system. Under Linux, its device name is enx+MAC (e.g. enxb03af2b6059f). This article shows what this network interface is for and how it can be deactivated if necessary, using a Supermicro H12SSL motherboard.
Network interface name basics
Network interfaces that begin with enx contain the MAC address as another part of the name. For more information, see the article Predictable Network Interface Names.
Purpose of the enx network interface on Supermicro motherboards
The virtual network interface is provided via RNDIS[1] Ethernet over USB and enables certain functions for communication between the operating system and BMC.[2] If you disable this Ethernet over USB interface, you cannot perform a server firmware update over in-band using Linux or Windows utilities (Supermicro Update Manager).
RNDIS Support in Linux
RNDIS support on Linux is expected to be discontinued in the future (as of October 2023).[3] The first Linux kernel version to be affected could be kernel 6.9.[4] We will update this section as soon as we have new relevant information on future support for communication between the Linux operating system and BMC on these Supermicro systems.
Network interfaces
In this example, the interface name of the virtual network interface is enxb03af2b6059f:
# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eno1: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 3c:ec:ef:6f:1f:3c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 10.2.2.160/24 brd 10.2.2.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute eno1
valid_lft 25261sec preferred_lft 25261sec
inet6 fe80::6880:fba7:7407:f7f7/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: eno2: <NO-CARRIER,BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 3c:ec:ef:6f:1f:3d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
7: enxb03af2b6059f: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether b0:3a:f2:b6:05:9f brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 169.254.3.1/24 brd 169.254.3.255 scope link dynamic noprefixroute enxb03af2b6059f
valid_lft 863543sec preferred_lft 863543sec
inet6 fe80::3346:74a7:85b3:a684/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Disable virtual network interface
The virtual network interface can be disabled either in the BMC web interface or via the operating system.
Note: DO NOT make the following changes while in-band operations are in progress, as this will cause the operations to abort:[2]
- DO NOT change the IP address of the virtual network interface.
- Do NOT disable the virtual network interface.
Configuration BMC web interface
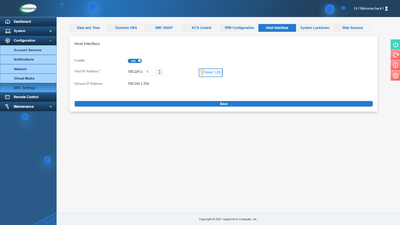
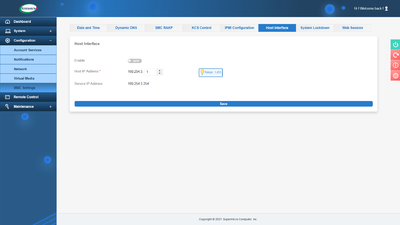
In the default configuration, the virtual network interface is enabled for communication between the operating system and BMC:
If you want to disable the virtual network interface, you can do so in the BMC web interface via Configuration ‣ BMC Settings ‣ Host Interface ‣ Off:
Disable via modprobe blacklist
When using Linux as the operating system, the virtual network interface can also be easily disabled by preventing the loading of the kernel module rndis_host.
To do this, simply create a file in /etc/modprobe.d/:
# echo "blacklist rndis_host" > /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-rndis_host.conf # cat /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-rndis_host.conf blacklist rndis_host # reboot
After the reboot, the virtual network interface is no longer active.
Command line outputs
The following outputs show the entries of the virtual network section which is provided by the rndis_host driver.
lsmod
# lsmod | grep -i rndis rndis_host 20480 0 cdc_ether 20480 1 rndis_host usbnet 45056 2 rndis_host,cdc_ether
lsusb -t
# lsusb -t
/: Bus 08.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 10000M
/: Bus 07.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 480M
|__ Port 1: Dev 2, If 0, Class=Hub, Driver=hub/5p, 480M
|__ Port 1: Dev 3, If 1, Class=Human Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 12M
|__ Port 1: Dev 3, If 0, Class=Human Interface Device, Driver=usbhid, 12M
|__ Port 2: Dev 7, If 0, Class=Wireless, Driver=rndis_host, 480M
|__ Port 2: Dev 7, If 1, Class=CDC Data, Driver=rndis_host, 480M
/: Bus 06.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 5000M
/: Bus 05.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 480M
/: Bus 04.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 5000M
/: Bus 03.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 480M
/: Bus 02.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 10000M
/: Bus 01.Port 1: Dev 1, Class=root_hub, Driver=xhci_hcd/2p, 480M
lsusb -s 007:007 -v
# lsusb -s 7:7 -v
Bus 007 Device 007: ID 0b1f:03ee Insyde Software Corp.
Device Descriptor:
bLength 18
bDescriptorType 1
bcdUSB 2.00
bDeviceClass 239 Miscellaneous Device
bDeviceSubClass 2 ?
bDeviceProtocol 1 Interface Association
bMaxPacketSize0 64
idVendor 0x0b1f Insyde Software Corp.
idProduct 0x03ee
bcdDevice 3.18
iManufacturer 1 Linux 3.18.0 with ast_vhub
iProduct 2 RNDIS/Ethernet Gadget
iSerial 0
bNumConfigurations 2
Configuration Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 2
wTotalLength 75
bNumInterfaces 2
bConfigurationValue 2
iConfiguration 0
bmAttributes 0xc0
Self Powered
MaxPower 2mA
Interface Association:
bLength 8
bDescriptorType 11
bFirstInterface 0
bInterfaceCount 2
bFunctionClass 224 Wireless
bFunctionSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
bFunctionProtocol 3 RNDIS
iFunction 6 RNDIS
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 224 Wireless
bInterfaceSubClass 1 Radio Frequency
bInterfaceProtocol 3 RNDIS
iInterface 4 RNDIS Communications Control
** UNRECOGNIZED: 05 24 00 10 01
** UNRECOGNIZED: 05 24 01 00 01
** UNRECOGNIZED: 04 24 02 00
** UNRECOGNIZED: 05 24 06 00 01
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0008 1x 8 bytes
bInterval 9
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 1
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 2
bInterfaceClass 10 CDC Data
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 5 RNDIS Ethernet Data
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0200 1x 512 bytes
bInterval 0
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x02 EP 2 OUT
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0200 1x 512 bytes
bInterval 0
Configuration Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 2
wTotalLength 88
bNumInterfaces 2
bConfigurationValue 1
iConfiguration 0
bmAttributes 0xc0
Self Powered
MaxPower 2mA
Interface Association:
bLength 8
bDescriptorType 11
bFirstInterface 0
bInterfaceCount 2
bFunctionClass 2 Communications
bFunctionSubClass 6 Ethernet Networking
bFunctionProtocol 0
iFunction 11 CDC ECM
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 0
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 1
bInterfaceClass 2 Communications
bInterfaceSubClass 6 Ethernet Networking
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 8 CDC Ethernet Control Model (ECM)
CDC Header:
bcdCDC 1.10
CDC Union:
bMasterInterface 0
bSlaveInterface 1
CDC Ethernet:
iMacAddress 9 b03af2b6059f
bmEthernetStatistics 0x00000000
wMaxSegmentSize 1514
wNumberMCFilters 0x0000
bNumberPowerFilters 0
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
bmAttributes 3
Transfer Type Interrupt
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0010 1x 16 bytes
bInterval 9
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 1
bAlternateSetting 0
bNumEndpoints 0
bInterfaceClass 10 CDC Data
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 0
Interface Descriptor:
bLength 9
bDescriptorType 4
bInterfaceNumber 1
bAlternateSetting 1
bNumEndpoints 2
bInterfaceClass 10 CDC Data
bInterfaceSubClass 0 Unused
bInterfaceProtocol 0
iInterface 10 CDC Ethernet Data
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x81 EP 1 IN
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0200 1x 512 bytes
bInterval 0
Endpoint Descriptor:
bLength 7
bDescriptorType 5
bEndpointAddress 0x02 EP 2 OUT
bmAttributes 2
Transfer Type Bulk
Synch Type None
Usage Type Data
wMaxPacketSize 0x0200 1x 512 bytes
bInterval 0
Device Qualifier (for other device speed):
bLength 10
bDescriptorType 6
bcdUSB 2.00
bDeviceClass 239 Miscellaneous Device
bDeviceSubClass 2 ?
bDeviceProtocol 1 Interface Association
bMaxPacketSize0 64
bNumConfigurations 2
Device Status: 0x0001
Self Powered
References
- ↑ RNDIS (en.wikipedia.org)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Extra virtual LAN (RNDIS ethernet over USB) (Supermicro FAQ 32374)
- ↑ Linux To Try Again To Disable All RNDIS Protocol Drivers (www.phoronix.com, 01.10.2023)
- ↑ Linux Still Working To Disable RNDIS Drivers In 2024 (www.phoronix.com, 19.02.2024)
|
Author: Werner Fischer Werner Fischer, working in the Knowledge Transfer team at Thomas-Krenn, completed his studies of Computer and Media Security at FH Hagenberg in Austria. He is a regular speaker at many conferences like LinuxTag, OSMC, OSDC, LinuxCon, and author for various IT magazines. In his spare time he enjoys playing the piano and training for a good result at the annual Linz marathon relay.
|